Are you sending your credentials to MitM without knowing it?
About a month ago, we reported that some phishing kits had added the capability of intercepting SMS-based 2FA tokens. Since then, we decided to look for more such tools and found a whopping 1200+ web-based phishing kits in our research, which are capable of intercepting 2FA when it is used by unsuspecting users.
These toolkits enable any wimpy “hacker” to utilize the MitM (Man-in-the-Middle) attacks.
After many major tech companies began requiring two-factor authentication as a standard security feature for their customers, these tools have grown to be quite popular in the cybercriminal underworld, facing a possibility that the leaked list of usernames and passwords have become worthless without being to 2FA.
In most situations, cybercrime organizations have used a Malware-type known as an “Infostealer” to obtain these authentication cookie files from computers that they had compromised. The problem is, that these are time based tokens, so unless threat actors act quickly, the stolen cookies become useless as well.
Welcome to the Man-in-the-Middle toolkits. Where the 2FA is, cookies are stolen while they are transmitted from the infected computer to the intended server (website or app).

So, what is the difference between Real-Time phishing and MitM phishing?
Well, you can read all about the Real-Time phishing in this article: So you think 2FA is protecting you… That’s cute
In a nutshell, real-time phishing is when the threat actor obtains a victim’s authentication cookie in REAL TIME, while the MitM approach is catching the victim during a session (cookie) theft.
Real-Time Phishing Explained
When a user types in their login and password on the phishing site, the attacker will then use these credentials to authenticate himself on the genuine site.
When the attacker is asked to authenticate using 2FA, he or she merely presses a button that requests the user for the real 2FA code, (received via email, SMS, or authenticator app), before collecting and entering the 2FA token on the actual site, establishing a genuine connection between their system and account.
Real Time phishing is useful for websites with short authentication windows like banking websites, where a few minutes of inactivity results in having to re-enter the authentication process all over. Therefore, collecting authentication cookies is useless. However, for websites such as email access, social media, and other services, these access cookies can be used for days, months or even years, without the end user even knowing about it.
This is where MitM phishing comes in..
This type of attack does not rely on the stolen cookies, instead, the attacker creates a reverse- proxie, where the traffic is sent to the cloud-based Phishing Toolkit server, that will relay information to the targeted web server or website, that the end user is trying to access. The website will trigger the 2FA code that will be sent to the user and the user will input this, again relaying it to the phishing toolkit cloud server. Let me help demonstrate how this would work.
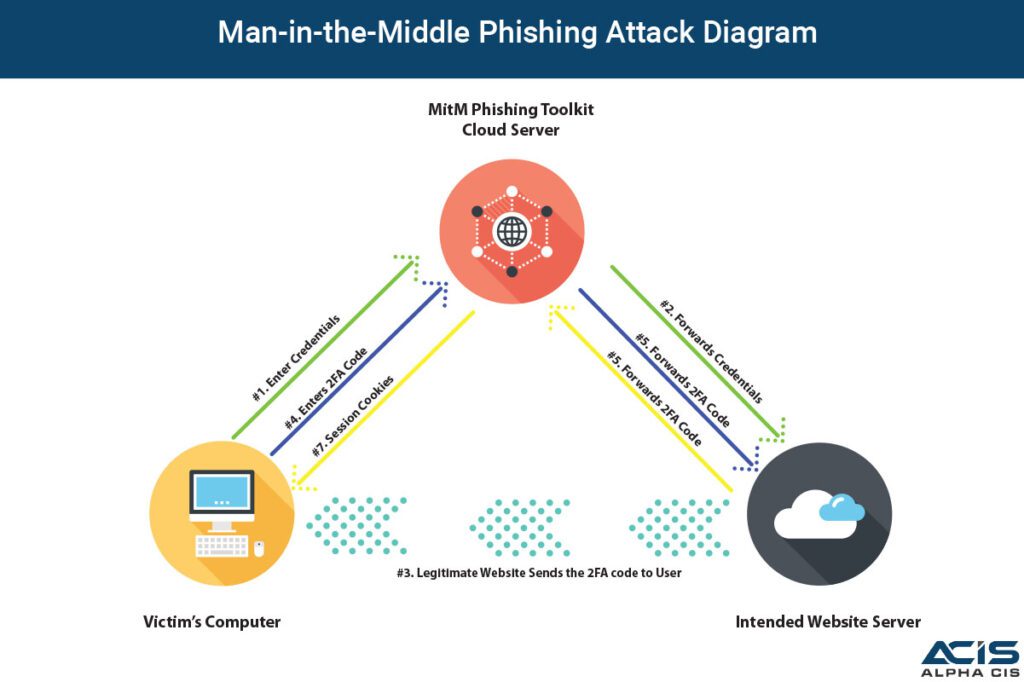
MitM Essentially just automates the whole phishing process for the attacker. These toolkits are wrapped into a nice, easy to use packages, that are easily implemented. This is why it’s important to limit what users can do on their computers. These toolkits often times attach to the browsers, or are installed as part of a wider malware loader that is downloaded from clicking on a malicious link.
If your business needs help securing your network from cyber threats reach out to a managed services provider or managed security provider such as AlphaCIS (678) 619-1218. We can perform a network scan, penetration testing, lock down permissions and ensure your systems are secure from internal and external threats.
Dmitriy Teplinskiy
I have worked in the IT industry for 15+ years. During this time I have consulted clients in accounting and finance, manufacturing, automotive and boating, retail and everything in between. My background is in Networking and Cybersecurity



