Picture this: It’s 3 AM at a major automotive plant, and an assembly line suddenly stops. In the old days, this would mean hours of downtime, frantic phone calls, and massive losses. But today? The plant’s information systems had already predicted this failure three days ago. Maintenance was scheduled, parts were ordered, and the “breakdown” became a planned 15-minute swap that actually improves overall efficiency.
This isn’t science fiction, it’s the reality of modern manufacturing in 2025. While we often focus on the impressive machinery, robotics, and automation that power today’s factories, there’s an invisible force that’s equally critical: information. Modern manufacturing runs on more than machines; it runs on information, and understanding this shift is crucial for any manufacturer looking to stay competitive.
Key Takeaways

Ready to Take IT Off Your Plate?
Stop worrying about downtime, security risks, or endless IT frustrations. AlphaCIS is the trusted IT partner for small and mid-sized businesses in Metro Atlanta, keeping systems secure, connected, and running the way they should every day.
Whether it’s preventing costly outages, protecting your data, or giving your team unlimited support, we make sure technology helps your business grow instead of holding it back.
📅 Book Your Free Consultation- Data is the new oil in manufacturing, driving everything from predictive maintenance to quality control and supply chain optimization
- Real-time information systems can reduce downtime by up to 50% and improve overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) by 25%
- Connected factories using IoT sensors and smart systems generate over 1TB of data daily, creating unprecedented opportunities for optimization
- Information-driven decision making enables manufacturers to respond to market changes 3x faster than traditional reactive approaches
- Integration of operational technology (OT) and information technology (IT) is essential for unlocking the full potential of modern manufacturing
The Information Revolution in Manufacturing
From Gut Feelings to Data-Driven Decisions
I remember visiting a family-owned manufacturing plant in Ohio five years ago. The plant manager, Jim, had been running operations for over 20 years. He could tell when a machine was about to fail just by listening to it. His intuition was impressive, but it wasn’t scalable or transferable to new employees.
Fast forward to my visit last month, the same plant now has sensors on every piece of equipment, collecting data on vibration, temperature, pressure, and performance metrics. Jim still works there, but now his experience is augmented by real-time data analytics that can predict failures weeks in advance.
This transformation illustrates a fundamental truth: modern manufacturing runs on more than machines; it runs on information that amplifies human expertise rather than replacing it.
The Data Explosion in Manufacturing
Today’s manufacturing facilities are data goldmines. Consider these staggering statistics:
– A single smart factory generates 1 terabyte of data daily
– IoT sensors in manufacturing are expected to reach 75 billion devices by 2025
– Companies using data analytics in manufacturing see 10-20% improvements in efficiency
– Predictive maintenance can reduce costs by 12-18% and eliminate up to 70% of breakdowns
But here’s the catch: having data isn’t the same as having information. Raw data needs to be processed, analyzed, and transformed into actionable insights.
Challenge 1: Breaking Down Information Silos
The Problem: Isolated Data Islands
One of the biggest challenges I see in manufacturing is the existence of information silos. Different departments, production, quality, maintenance, and supply chain often use separate systems that don’t communicate with each other.
Imagine trying to optimize production when:
– Your production system doesn’t talk to your inventory management
– Quality data sits isolated from production metrics
– Maintenance schedules aren’t integrated with production planning
– Customer demand forecasts don’t reach the shop floor in real-time
Why It Matters
Information silos create several critical problems:
Delayed Decision Making
When data doesn’t flow freely, managers make decisions based on incomplete information, often too late to prevent problems.
Inefficient Resource Allocation
Without integrated information, companies overstock some materials while running short on others, leading to increased costs and production delays.
Missed Optimization Opportunities
The most significant improvements often come from optimizing across departments, which is impossible when information is siloed.
The Solution: Integrated Information Systems
The answer lies in creating connected information ecosystems where data flows seamlessly across all manufacturing functions.
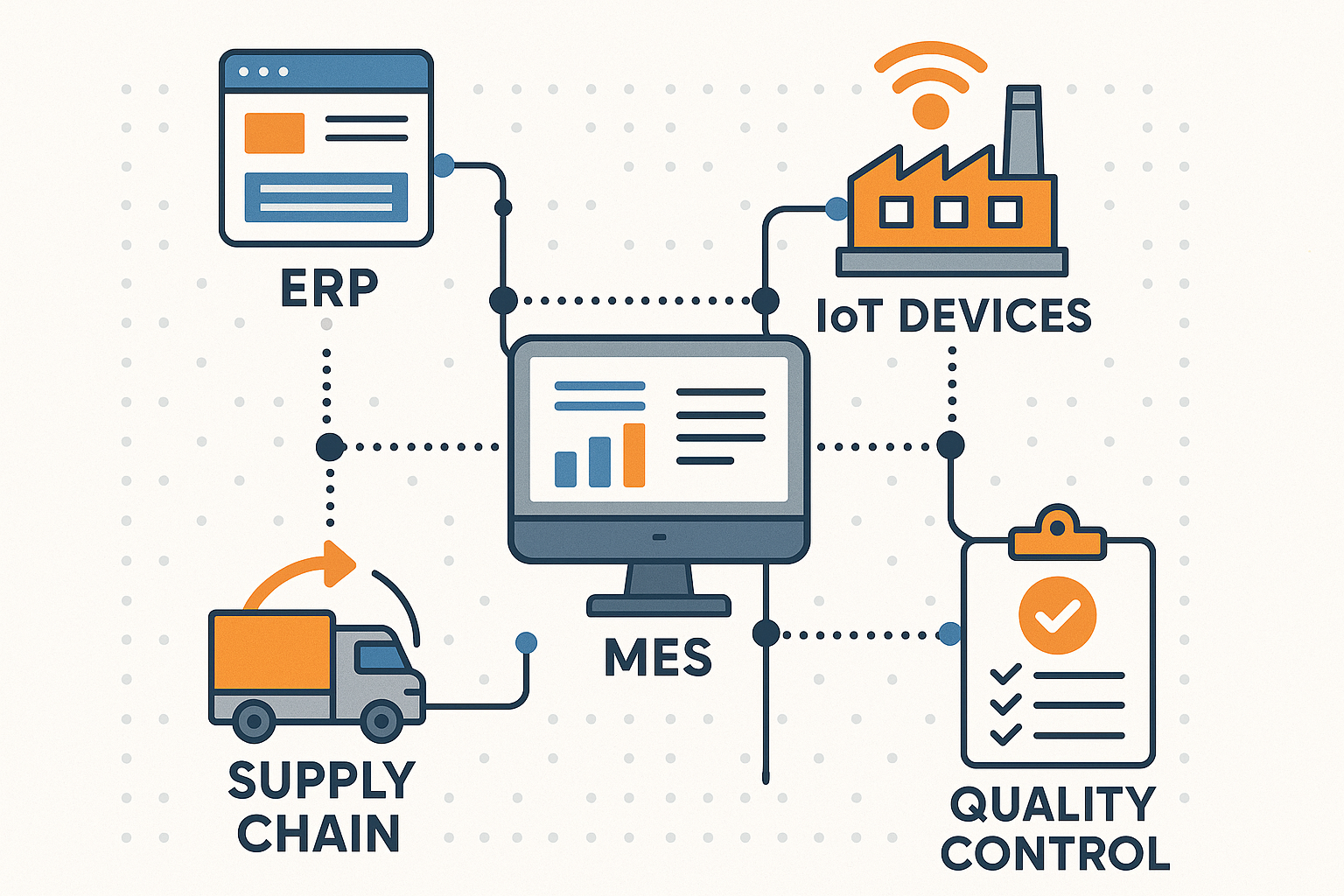
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Integration
Modern ERP systems serve as the backbone, connecting finance, operations, supply chain, and customer management in one unified platform.
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES)
MES bridges the gap between ERP and shop floor operations, providing real-time visibility into production processes.
Internet of Things (IoT) Connectivity
IoT sensors and devices collect data from equipment, environmental conditions, and products themselves, feeding this information into centralized systems.
> “Information is the oil of the 21st century, and analytics is the combustion engine.” – Peter Sondergaard, Gartner
Challenge 2: Real-Time Visibility and Control
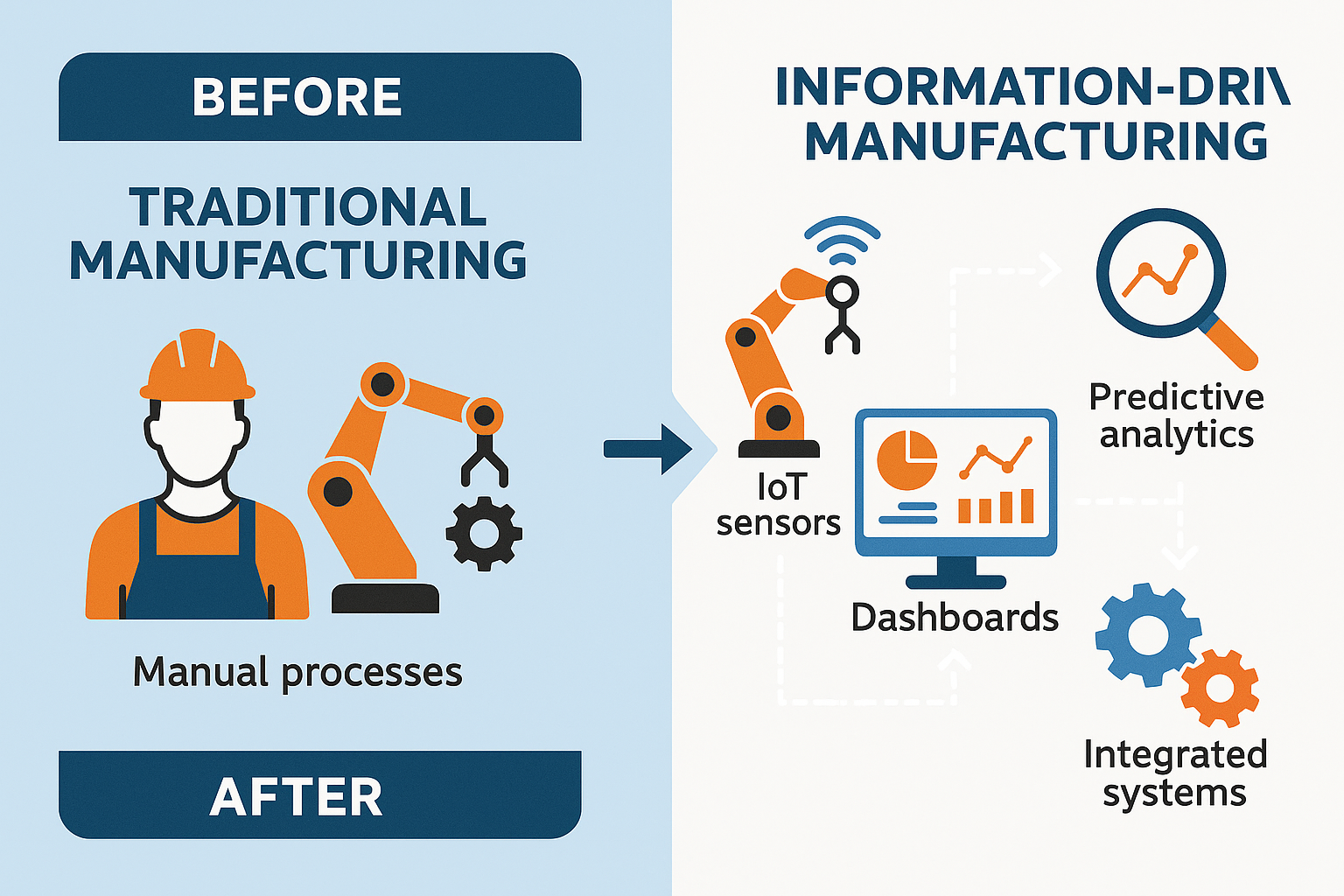
The Problem: Flying Blind
Many manufacturers still operate with limited real-time visibility into their operations. They might know what happened yesterday or last week, but they don’t know what’s happening right now.
I worked with an electronics manufacturer who discovered they were making defective products for six hours before anyone noticed. By then, they had produced 2,400 units that needed to be scrapped, costing them over $180,000.
Why Real-Time Information Matters
Immediate Problem Detection
Real-time monitoring allows for instant detection of quality issues, equipment problems, or process deviations.
Dynamic Optimization
With real-time data, manufacturers can adjust production parameters on the fly to optimize efficiency, quality, and resource utilization.
Agile Response to Changes
Market demands, supply chain disruptions, or customer requirements can change rapidly. Real-time information enables quick adaptation.
The Solution: Real-Time Manufacturing Intelligence
Digital Dashboards
Create comprehensive dashboards that display key performance indicators (KPIs) in real-time, accessible to relevant stakeholders across the organization.
Automated Alerts and Notifications
Set up intelligent alerting systems that notify the right people when parameters exceed acceptable ranges or when immediate action is required.
Mobile Accessibility
Ensure that critical information is accessible on mobile devices, allowing managers and technicians to stay connected even when away from their desks.
Challenge 3: Predictive Analytics and Maintenance
The Problem: Reactive Maintenance Culture
Traditional manufacturing operates on a reactive maintenance model, fixing things when they break. This approach leads to:
– Unexpected downtime
– Higher repair costs
– Safety risks
– Production delays
– Customer dissatisfaction
The Information-Driven Solution
Predictive Maintenance Using Machine Learning
Modern manufacturing runs on more than machines; it runs on information that can predict the future. Machine learning algorithms analyze patterns in equipment data to predict failures before they occur.
Key components include:
Condition Monitoring
– Vibration analysis
– Temperature monitoring
– Oil analysis
– Electrical signature analysis
Data Analytics Platforms
– Historical trend analysis
– Anomaly detection
– Failure pattern recognition
– Maintenance scheduling optimization
Integration with Work Management Systems
– Automatic work order generation
– Parts inventory management
– Technician scheduling
– Performance tracking
Real-World Success Story
A major steel manufacturer implemented predictive maintenance across their rolling mills. The results were impressive:
– 47% reduction in unplanned downtime
– 25% decrease in maintenance costs
– $2.3 million annual savings from improved equipment reliability
– 15% improvement in overall equipment effectiveness (OEE)
Challenge 4: Supply Chain Information Integration
The Problem: Supply Chain Blind Spots
Supply chains have become increasingly complex, with multiple suppliers, logistics providers, and distribution channels. Without proper information integration, manufacturers face:
– Inventory imbalances (too much of some materials, not enough of others)
– Supplier performance issues that go undetected until they cause problems
– Demand forecasting errors due to a lack of real-time market data
– Logistics inefficiencies from poor coordination
The Information Solution: Connected Supply Networks
Supplier Integration Platforms
Connect directly with supplier systems to get real-time updates on:
– Order status and delivery schedules
– Quality metrics and certifications
– Capacity and capability changes
– Risk factors and contingency plans
Demand Sensing Technology
Use advanced analytics to process multiple data sources:
– Point-of-sale data from customers
– Social media sentiment analysis
– Economic indicators
– Weather patterns
– Market trends
Logistics Optimization
Integrate with logistics providers to optimize:
– Route planning and scheduling
– Warehouse management
– Inventory positioning
– Transportation costs
Case Study: Automotive Manufacturer
A leading automotive manufacturer integrated their supply chain information systems and achieved:
– 30% reduction in inventory holding costs
– 95% improvement in on-time delivery performance
– $15 million annual savings from optimized logistics
– 50% faster response to supply chain disruptions
Challenge 5: Quality Information Systems
The Problem: Quality as an Afterthought
Many manufacturers still treat quality as a final inspection step rather than an integrated part of the entire production process. This approach leads to:
– High scrap and rework costs
– Customer complaints and returns
– Regulatory compliance issues
– Brand reputation damage
The Information-Driven Quality Revolution
Statistical Process Control (SPC) 2.0
Modern SPC systems go beyond traditional control charts:
– Real-time data collection from in-line sensors
– Automated analysis and trend detection
– Predictive quality alerts before defects occur
– Root cause analysis using machine learning
Traceability and Genealogy
Complete product traceability requires sophisticated information systems:
– Raw material tracking from supplier to finished product
– Process parameter recording at each manufacturing step
– Quality test results linked to specific units
– Customer feedback connected to production data
Quality Analytics Platforms
Advanced analytics help identify quality improvement opportunities:
– Correlation analysis between process parameters and quality outcomes
– Supplier quality performance trending
– Customer complaint pattern analysis
– Cost of quality optimization
Challenge 6: Workforce Information and Training
The Problem: Skills Gap in Information-Rich Environments
As manufacturing becomes more information-driven, the workforce needs new skills:
– Data literacy to interpret and act on information
– Digital tool proficiency to use modern manufacturing systems
– Problem-solving abilities enhanced by data analytics
– Continuous learning mindset to adapt to evolving technologies
The Solution: Information-Enabled Workforce Development
Digital Training Platforms
– Interactive learning modules
– Virtual reality training simulations
– Micro-learning for just-in-time skill development
– Performance tracking and competency management
Augmented Reality (AR) Work Instructions
– Step-by-step visual guidance
– Real-time information overlay
– Remote expert assistance
– Error prevention and quality assurance
Knowledge Management Systems
– Capture and share institutional knowledge
– Best practice documentation
– Troubleshooting guides and procedures
– Continuous improvement tracking
The Technology Stack: Building Information-Driven Manufacturing
Core Technologies Enabling Information-Rich Manufacturing
Edge Computing
Processing data closer to where it’s generated:
– Reduced latency for real-time decisions
– Lower bandwidth requirements
– Improved security and data privacy
– Continued operation during network disruptions
Cloud Platforms
Scalable infrastructure for data storage and analytics:
– Elastic computing resources
– Advanced analytics and AI capabilities
– Global accessibility and collaboration
– Disaster recovery and backup
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Transforming data into intelligent insights:
– Pattern recognition in complex datasets
– Predictive modeling and forecasting
– Automated decision-making
– Continuous learning and improvement
Digital Twins
Virtual representations of physical manufacturing systems:
– Real-time simulation and modeling
– Scenario testing and optimization
– Predictive analysis and planning
– Training and education platforms
Ready to Take IT Off Your Plate?
Stop worrying about downtime, security risks, or endless IT frustrations. AlphaCIS is the trusted IT partner for small and mid-sized businesses in Metro Atlanta, keeping systems secure, connected, and running the way they should every day.
Whether it’s preventing costly outages, protecting your data, or giving your team unlimited support, we make sure technology helps your business grow instead of holding it back.
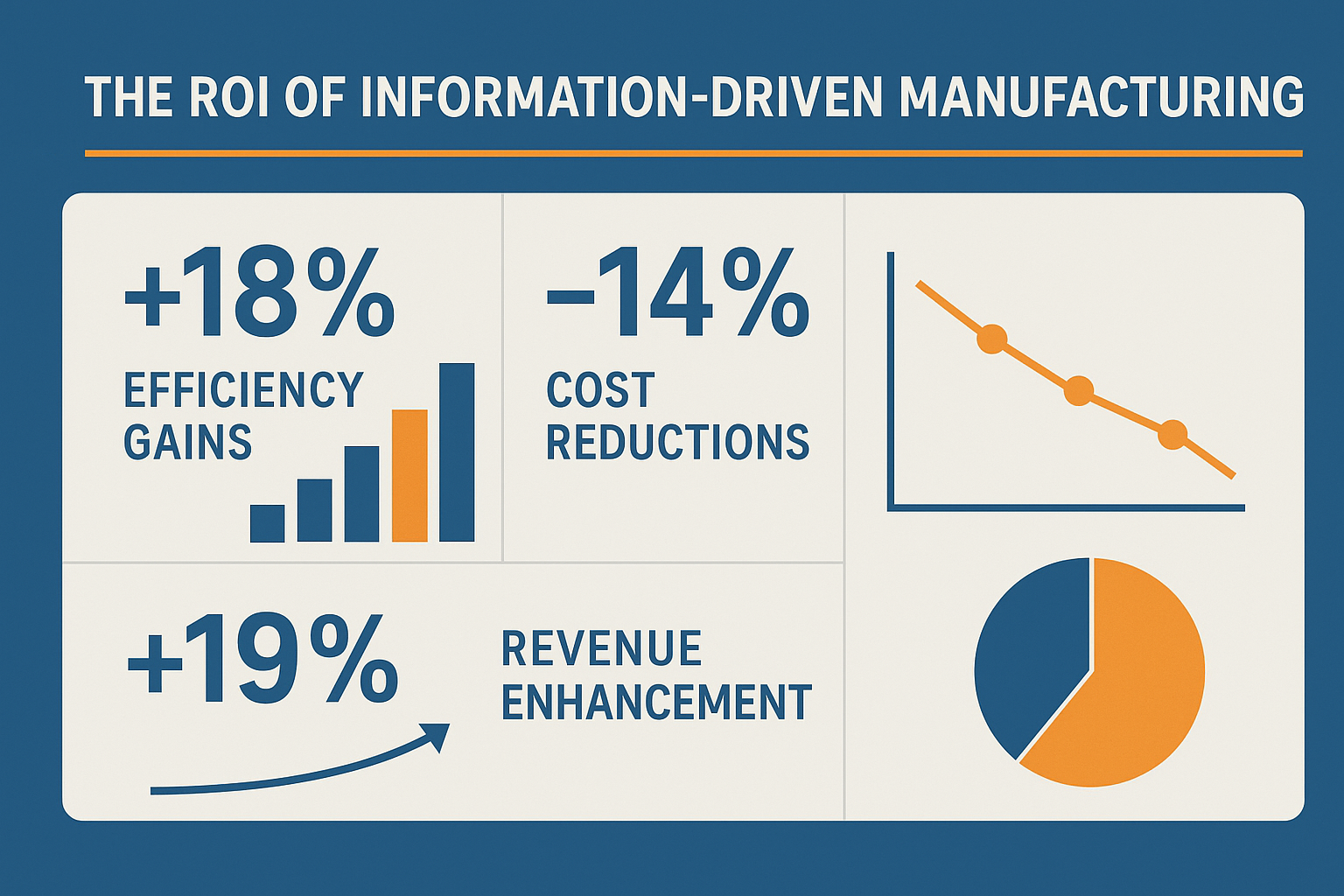
📅 Book Your Free ConsultationThe ROI of Information-Driven Manufacturing
Quantifying the Benefits
Let’s talk numbers. When manufacturers embrace the principle that modern manufacturing runs on more than machines, it runs on information, they see measurable returns:
Operational Efficiency Gains
– 15-25% improvement in Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
– 10-20% reduction in energy consumption
– 20-30% decrease in inventory holding costs
– 25-35% improvement in on-time delivery performance
Cost Reduction Opportunities
– 12-18% reduction in maintenance costs through predictive strategies
– 5-15% decrease in quality costs through real-time monitoring
– 10-25% reduction in labor costs through automation and optimization
– 20-40% decrease in unplanned downtime
Revenue Enhancement
– Faster time-to-market for new products
– Improved customer satisfaction and retention
– New revenue streams from data-driven services
– Enhanced competitiveness in the marketplace
Real-World ROI Example
A mid-sized aerospace manufacturer invested $2.8 million in information systems and digital transformation over 18 months. Their results:
Year 1 Results:
– $1.2 million savings from reduced downtime
– $800,000 savings from inventory optimization
– $600,000 savings from improved quality
– Total Year 1 ROI: 93%
Year 2 and Beyond:
– $3.5 million annual recurring savings
– 40% faster product development cycles
– 25% improvement in customer satisfaction scores
– Ongoing ROI: 125% annually
Building Your Information-Driven Manufacturing Strategy
Step 1: Assess Your Current State
Before implementing new information systems, conduct a thorough assessment:
Technology Audit
– Inventory existing systems and their capabilities
– Identify integration gaps and data silos
– Evaluate data quality and accessibility
– Assess cybersecurity and compliance status
Process Analysis
– Map current information flows
– Identify manual processes that could be automated
– Document decision-making processes
– Analyze performance metrics and KPIs
Skills Assessment
– Evaluate workforce digital literacy
– Identify training and development needs
– Assess change management capabilities
– Plan for organizational transformation
Step 2: Develop Your Information Architecture
Data Strategy
Define what data you need, how you’ll collect it, store it, and use it:
– Production and process data
– Quality and compliance information
– Supply chain and logistics data
– Customer and market intelligence
Technology Stack Planning
Choose technologies that align with your business objectives:
– Cloud vs. on-premise infrastructure
– Integration platforms and middleware
– Analytics and AI capabilities
– Security and compliance tools
Governance Framework
Establish policies and procedures for:
– Data ownership and stewardship
– Privacy and security protocols
– System access and user management
– Change management processes
Step 3: Implementation Roadmap
Phase 1: Foundation (Months 1-6)
– Implement core ERP and MES systems
– Deploy basic IoT sensors and data collection
– Establish a data governance framework
– Begin workforce training programs
Phase 2: Integration (Months 7-12)
– Connect systems for seamless data flow
– Implement real-time dashboards and reporting
– Deploy predictive maintenance capabilities
– Expand sensor deployment
Phase 3: Optimization (Months 13-18)
– Implement advanced analytics and AI
– Develop digital twin capabilities
– Integrate supply chain partners
– Launch continuous improvement programs
Phase 4: Innovation (Months 19+)
– Explore autonomous manufacturing systems
– Develop new data-driven business models
– Lead industry innovation initiatives
– Scale successful implementations
Overcoming Common Implementation Challenges
Challenge: Resistance to Change
The Reality: People are often hesitant to adopt new information systems, especially if they’ve been successful with traditional methods.
The Solution:
– Involve employees in the planning and implementation process
– Provide comprehensive training and ongoing support
– Demonstrate quick wins to build confidence and momentum
– Communicate the benefits clearly and consistently
Challenge: Integration Complexity
The Reality: Manufacturing environments often have legacy systems that are difficult to integrate with modern information platforms.
The Solution:
– Start with pilot projects to prove concepts and build expertise
– Use middleware and integration platforms to bridge legacy and modern systems
– Plan for gradual migration rather than complete system replacement
– Work with experienced integration partners who understand manufacturing environments
Challenge: Data Quality Issues
The Reality: Poor data quality can undermine even the most sophisticated information systems.
The Solution:
– Implement data validation at the point of collection
– Establish data cleansing processes for historical information
– Create data quality metrics and monitoring systems
– Train employees on the importance of accurate data entry
Challenge: Cybersecurity Concerns
The Reality: Connected manufacturing systems create new cybersecurity vulnerabilities that must be addressed.
The Solution:
– Implement defense-in-depth security strategies
– Segregate operational and business networks where appropriate
– Regular security assessments and penetration testing
– Employee training on cybersecurity best practices
The Future of Information-Driven Manufacturing
Emerging Technologies and Trends
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI will become even more sophisticated, enabling:
– Autonomous quality control and process optimization
– Self-healing manufacturing systems
– Intelligent supply chain orchestration
– Predictive customer demand modeling
Edge Computing and 5G
These technologies will enable:
– Ultra-low latency decision making
– Massive IoT device connectivity
– Real-time video analytics and computer vision
– Distributed intelligence across manufacturing networks
Blockchain and Distributed Ledgers
Blockchain technology will provide:
– Immutable supply chain traceability
– Secure data sharing between partners
– Automated smart contracts for transactions
– Enhanced cybersecurity for industrial systems
Augmented and Virtual Reality
AR/VR will transform:
– Workforce training and skill development
– Remote maintenance and troubleshooting
– Design and prototyping processes
– Customer collaboration and support
Preparing for the Future
Continuous Learning Culture
Foster an environment where:
– Employees are encouraged to learn new technologies
– Experimentation and innovation are rewarded
– Knowledge sharing is promoted across the organization
– External partnerships provide access to cutting-edge capabilities
Flexible Technology Architecture
Build systems that can:
– Adapt to changing business requirements
– Integrate with emerging technologies
– Scale up or down based on demand
– Support new business models and revenue streams
Strategic Partnerships
Develop relationships with:
– Technology vendors and system integrators
– Research institutions and universities
– Industry consortia and standards bodies
– Startup companies with innovative solutions
Final CTA: Transform Your Manufacturing Future
The message is clear: modern manufacturing runs on more than machines; it runs on information. The companies that embrace this reality today will be the leaders of tomorrow.
Don’t let your competitors gain the advantage while you’re still relying on outdated approaches. The time to act is now.
Conclusion
The transformation from traditional manufacturing to information-driven operations isn’t just a technological upgrade; it’s a fundamental shift in how we think about manufacturing excellence. As we’ve explored throughout this article, modern manufacturing runs on more than machines; it runs on information that enables smarter decisions, predictive capabilities, and unprecedented levels of efficiency.
The manufacturers who recognize this shift and act on it will thrive in the competitive landscape of 2025 and beyond. Those who don’t risk being left behind by more agile, information-savvy competitors.
The journey may seem daunting, but remember that every step toward information-driven manufacturing delivers value. Start with small pilot projects, build on your successes, and gradually expand your capabilities. The key is to begin now and maintain momentum.
Your machines are important, but your information systems are what will truly differentiate your manufacturing operation in the digital age. The future belongs to manufacturers who understand that information is the invisible force that powers modern manufacturing excellence.
Take the first step today. Your future success depends on the information-driven decisions you make right now.
Ready to Take IT Off Your Plate?
Stop worrying about downtime, security risks, or endless IT frustrations. AlphaCIS is the trusted IT partner for small and mid-sized businesses in Metro Atlanta, keeping systems secure, connected, and running the way they should every day.
Whether it’s preventing costly outages, protecting your data, or giving your team unlimited support, we make sure technology helps your business grow instead of holding it back.
📅 Book Your Free Consultation
Dmitriy Teplinskiy
I have worked in the IT industry for 15+ years. During this time I have consulted clients in accounting and finance, manufacturing, automotive and boating, retail and everything in between. My background is in Networking and Cybersecurity



